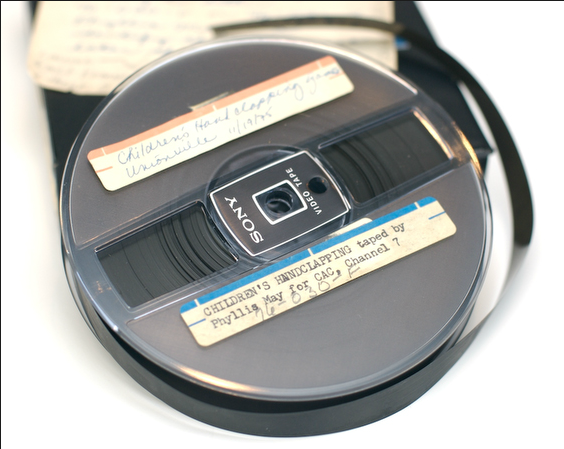

1/2 inch, consumer, open reel video format used in the 1960s-70s. This format suffers from Sticky Shed Syndrome, making playback difficult. Working machines for this long-obsolete format are scarce. Source: IUB Media Preservation Initiative, used with permission. Note: IUB has asked me to stress that the above photo is not representative of all media collections at the university.
The Media Preservation Site at Indiana University – Bloomington (IUB) makes its message loud and clear the moment you first set your eyes on it: “Our History is At Risk.”
Home to at least 3 million media objects, including sound and moving image recordings, photos, documents, and artifacts, IUB has come to grips with the issue at hand: a great deal of their heritage is locked within obsolete electronic and analog playback formats for sound and moving images. As an old format becomes obsolete, it gets harder by the day to find working equipment to play back these objects. And that assumes that the objects can be played back, not having succumbed to age, wear and physical decay. Lacquer from old aluminum audio discs can delaminate, making them unplayable. Video tapes from the 1960s, 70s and 80s can suffer from a condition where the binding agent that holds the recording material to the plastic base sheds, allowing audio and video recordings to literally flake into nothingness. Film, too, has its own serious decay problems.
With its vast collection, faculty and staff at IUB knew the situation could become serious if nothing was done. Their first step was to take stock of the situation, and consult outside experts (myself included) to get input how how best to address the problem.
Their efforts began nearly 18 months ago when a group of IUB faculty and staff, concerned about the potential fate of important special collections on campus, approached their Office of the Vice Provost for Research about the critical issues of media, and to impress upon them that time was of the essence to address these issues.
“Even though [IU Bloomington’s] needs are now documented, and it is far better equipped than most universities in the country to meet them, there is no guarantee that IU can adequately preserve its collections in the near future.”
— The State of Recorded Sound Preservation in the United States, Council on Library and Information Resources for The Library of Congress, Washington
The culmination of their efforts to date have been documented on the IUB Media Preservation Website, where they document their comprehensive effort to preserve IUB’s vast audio, video, and film holdings. Some important documents from their study and efforts including IUB’s Director of Media Preservation Services Mike Casey‘s Media Preservation Survey (PDF), outlining the collection holders, preservation stakeholders, the risks involved, and potential preservation strategies. A follow-on public report (12MB PDF) also lays out the situation and what steps are being taken to save their special collections and historic content. Continued engagement, updates, and discussion on decisions made and procedures undertaken are regularly made available on their Media Preservation Blog.
The IUB Media Preservation Blog
IUB has many years of work ahead of it, not only to transfer older content into more modern digital formats, but also to continue to maintain those archives, preserve new content, and keep pace with new technologies and formats to ensure that their collections are accessible. It’s encouraging to see them in action, and their efforts stand as a potential framework for other organizations in a similar bind to model their initiatives after.
